Much like a real life firewall protects a building from the damage of flames, a virtual firewall on a computer or network system acts as a barrier between harmful cyber activities (viruses, phishing, hacking, etc.) and the sensitive information contained on your computers and network. But how do firewalls work? What types of firewalls are available? How easily can they be managed? The answers to all these questions lie below.
Firewalls Explained
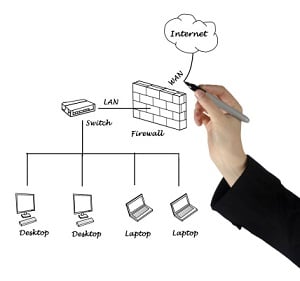 In its simplest form, a firewall is a system that controls access to your computer and/or network using a set of control policies and settings. The purpose of a firewall is to filter any traffic coming into your network from the outside. Acting as a transit point, the firewall controls access to your network by filtering all inbound network traffic and determining which data packets might be harmful.
In its simplest form, a firewall is a system that controls access to your computer and/or network using a set of control policies and settings. The purpose of a firewall is to filter any traffic coming into your network from the outside. Acting as a transit point, the firewall controls access to your network by filtering all inbound network traffic and determining which data packets might be harmful.
A firewall is a tool that is highly customizable. Its filtering strength can be increased or decreased based on your security requirements. While it is possible to loosen and tighten these controls, it is generally a good idea to tighten controls when more traffic or users are accessing your network. The type of firewall you use and the manner in which it is configured are all factors that should be considered when establishing a business network firewall.
Types of Firewalls
There are a myriad of firewall options available for personal and business use, but there are three particular systems that are considered the most common today. These include a stateless firewall, statefull firewall and a packet-filtering firewall. The definitions that follow require a fairly advanced understanding of this technology – if you have any questions, talk to a Business IT specialist or post your questions in the comments below.
The stateless firewall was one of the first to be launched to protect computers and networks from malware and other malicious content. Stateless firewalls filter and inspect packets of inbound data using preset acceptance protocols. Should the packet of data fail to meet the parameters set forth in the protocol, it is dropped from the network and denied access.
With a statefull firewall, the system will filter incoming data packets once they are stored in the firewall by judging the flow of information. Once the packet is stored, the firewall can compare the packet to any existing flow of data on the network to see if it matches up anywhere and determine its threat risk at that point.
A packet-filtering firewall analyzes information contained in different layers of the data packet and then allows or denies access to the network based upon factors such as destination IP address, protocol, packet source or packet type.
For businesses with larger networks and several computers, a Unified Threat Management (UTM) system is an additional option that offers a comprehensive security solution. It expands upon the traditional firewall solutions by combining additional security capabilities including SPAM filtering, antivirus protection and more. It connects to your business network directly and filters all incoming traffic on the network and compares it to the varying needs of different computers and users on the network to determine access.
Firewall Management
The manner in which a firewall is managed is something that needs to be taken into consideration by businesses as well. The above information covered types of firewalls, while we’ll now explain the management of these systems. There are three typical types of firewall management: unmanaged dedicated, managed dedicated and hosted firewalls.
Unmanaged dedicated firewalls are those which are installed locally on your business network and used specifically for your network needs and no others. This ensures a high level of security but requires a strong in-house IT department to manage the system.
Managed dedicated firewalls differ from unmanaged dedicated firewalls only in the fact that your business is not responsible for purchasing and maintaining equipment. You get the same high level of security dedicated to your network, but a business IT service provider manages your network security.
Finally, there is the option of using a hosted firewall. This type of management is done entirely from a virtual system on a shared infrastructure platform. Your business neither invests in equipment nor spends money on IT employees to manage firewall security.
Role of Business IT Service Providers
If you are confused by all these different firewall terms, you aren’t alone. Consulting a business IT service provider is the best way to determine which type of firewall and firewall management will best suit your business. Professionals from an IT service provider can assess the needs and capabilities of your business and help you determine which firewall solutions will be the best fit for your network.
